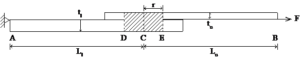Stress Intensity Factor Solutions for Similar and Dissimilar Spot Welds in Lap-Shear Specimens under Clamped Loading Conditions
Shin-Jang Sung and Jwo Pan
Lap-shear specimens are commonly used to evaluate the fracture and fatigue strengths of similar and dissimilar welds. The stress intensity factor solutions are useful to correlate with the fatigue lives of these welds. The stress intensity factor solutions for similar and dissimilar welds in lap-shear specimens of equal and unequal thickness under pinned and clamped loading conditions are examined by computational and analytical solutions. Both computational and analytical solutions indicate that the bending moments and the transverse shear forces at the clamped edges can reduce the stress intensity factor solutions for a given specimen geometry by about 7% for similar welds and by about 20% for dissimilar aluminum/steel and magnesium/steel welds when compared to those under pinned loading conditions. The analytical and computational stress intensity factor solutions suggest that the fatigue lives of the welds in lap-shear specimens under clamped loading conditions are higher than those under pinned loading conditions.
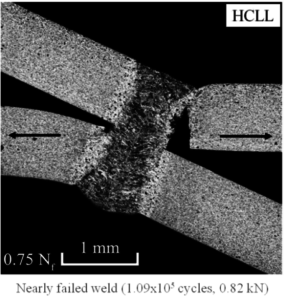
Figure 1. Optical micrographs of the cross section along the symmetry plane of a failed weld in a specimen of high strength low alloy sheets under cyclic loading conditions.
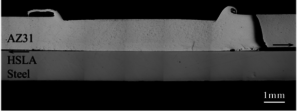
Figure 2. Optical micrographs of the cross section along the symmetry plane of a failed ultrasonic weld in a specimen of magnesium and steel sheets.
Figure 3. A lap-shear specimen with a weld under pinned loading conditions.
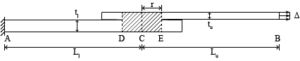
Figure 4. A lap-shear specimen with a weld under clamped loading conditions.
- S.-J. Sung and J. Pan, “Further Investigation of Stress Intensity Factor Solutions for Similar and Dissimilar Welds in Lap-Shear Specimens under Clamped Loading Conditions,” Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Vol. 166, 2016, pp. 60-81. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2016.08.016. (EFM 2016 2D Clamped)