Failure Mode and Fatigue Behavior of Dissimilar Laser Welds in Lap-Shear Specimens of Aluminum and Copper Sheets
William Lai, Shin-Jang Sung, Jwo Pan, Yunan Guo (Ford) and Xuming Su (Ford)
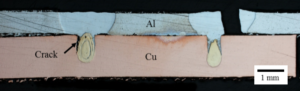
Failure mode and fatigue behavior of dissimilar laser welds in lap-shear specimens of aluminum and copper sheets are investigated. Quasi-static tests and fatigue tests of laser-welded lap-shear specimens under different load ranges with the load ratio of 0.1 were conducted. Optical micrographs of the welds after the tests were examined to understand the failure modes of the specimens. For the specimens tested under quasi-static loading conditions, the micrograph indicates that the specimen failed through the fusion zone of the aluminum sheet. For the specimens tested under cyclic loading conditions, two types of failure modes were observed under different load ranges. One failure mode has a kinked crack initiating from the interfacial surface between the aluminum and copper sheets and growing into the aluminum fusion zone at an angle close to 90°. The other failure mode has an interfacial crack initiating at the interfacial surface between the aluminum and copper sheets and growing along the interfacial surface between the fusion zone and the copper base metal at an angle close to 90°. In general, the fatigue lives are longer for the specimens failed through the copper sheet than those failed through the aluminum fusion zone.

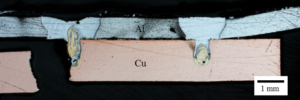
Figure 1. A top view of a laser-welded lap-shear specimen after machining.
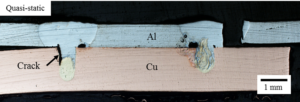
Figure 2. Optical micrographs of the cross sections along the symmetry planes of a failed specimen under quasi-static loading conditions.
Figure 3. Optical micrographs of the cross sections along the symmetry planes of (a) a failed specimen at the fatigue life of 2.3×104 cycles under a load range of 416 N and (b) a failed specimen at the fatigue life of 1.2×105 cycles under a load range of 416 N.
Figure 4. Experimental results of the fatigue tests for the laser-welded lap-shear specimens under the load ratio of 0.1.
- W.-J. Lai, S.-J. Sung, J. Pan, Y. Guo, and X. Su, 2014, “Failure Mode and Fatigue Behavior of Dissimilar Laser Welds in Lap-Shear Specimens of Aluminum and Copper Sheets,” SAE International Journal of Materials and Manufacturing 7(3), pp. 706-710, . DOI: 10.4271/2014-01-1986. (SAE 2014-01-1986)